Advancements in radiation glass technology for better protection
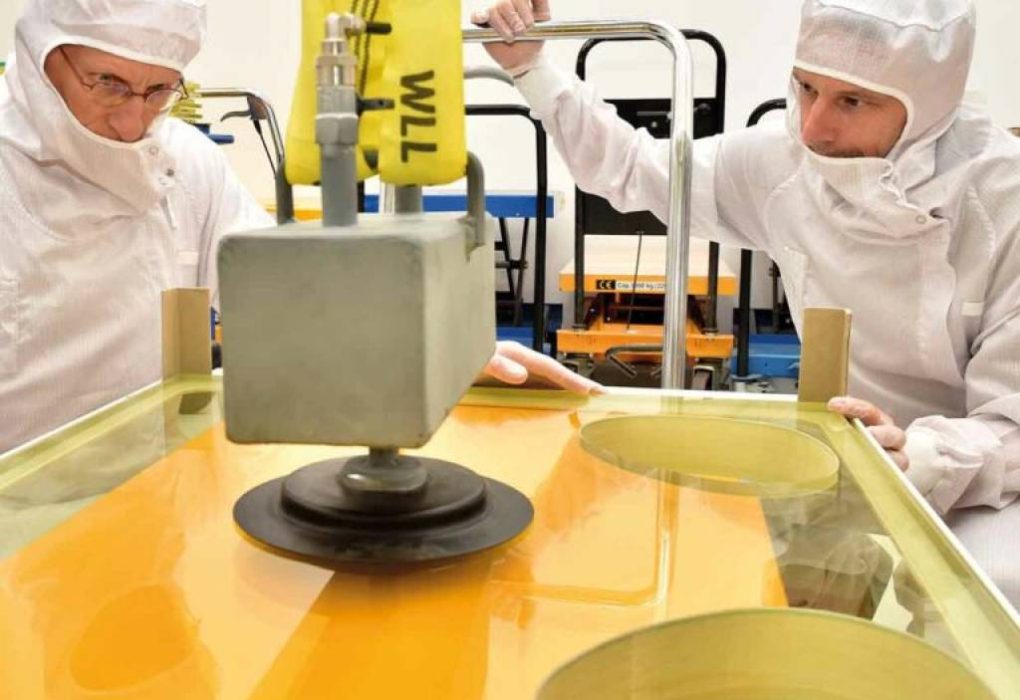
Understanding Radiation Glass Technology Radiation glass technology plays a crucial role in ensuring safety across medical, industrial, and research fields. As exposure to ionizing radiation poses significant health risks, advancements in this technology aim to enhance protection while maintaining optimal visibility and durability. Traditionally, radiation shielding was achieved using leaded glass, known for its dense…
How mobile radiation affects your health and how to stay safe
Understanding Mobile Radiation and Its Impact on Health With the widespread use of mobile phones, concerns about the potential health effects of radiation exposure have increased. Mobile devices emit electromagnetic fields (EMFs), which can penetrate the human body and potentially lead to adverse health effects. While ongoing research aims to uncover definitive conclusions, many studies…

The best exercises to improve your posture and appear taller
Why Posture Matters for Your Appearance Maintaining good posture is crucial, not only for your spine's health but also for your overall appearance. Poor posture, such as slouching or a rounded back, tends to compress your body, making you look shorter and less confident. On the other hand, standing tall with good posture can make…
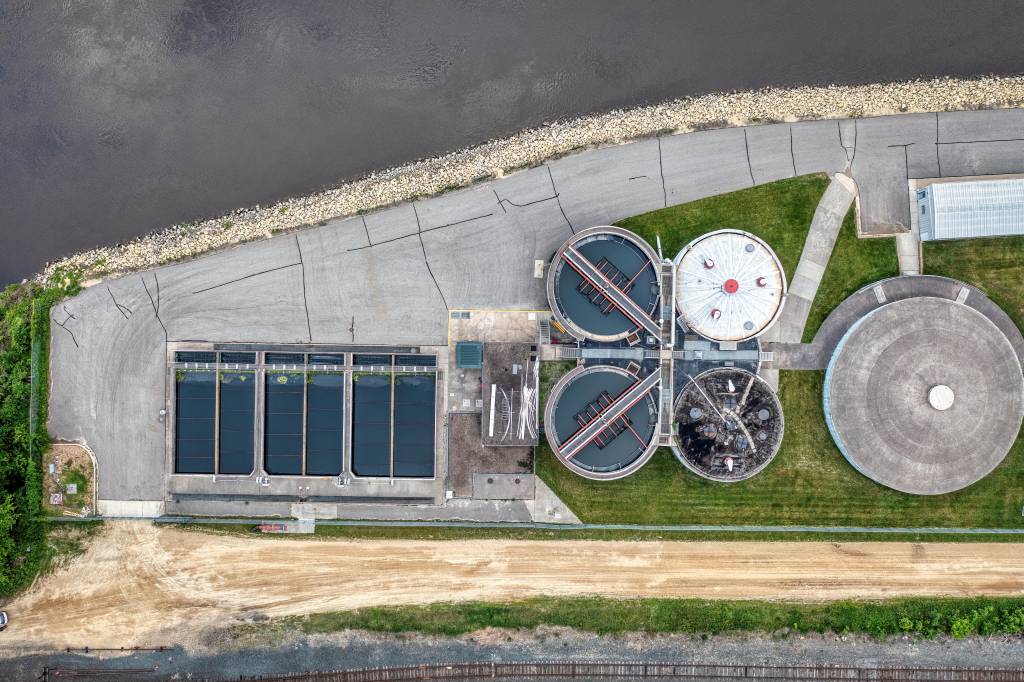

Water Reuse: An Innovative Solution for a Thirsty Planet
Understanding Water Reuse Water reuse, also known as water recycling or reclamation, refers to the process of treating wastewaters to make them safe and suitable for various applications. This innovative solution is becoming increasingly crucial as the global demand for clean water rises. From agricultural irrigation to industrial processes and even potable uses, water reuse…

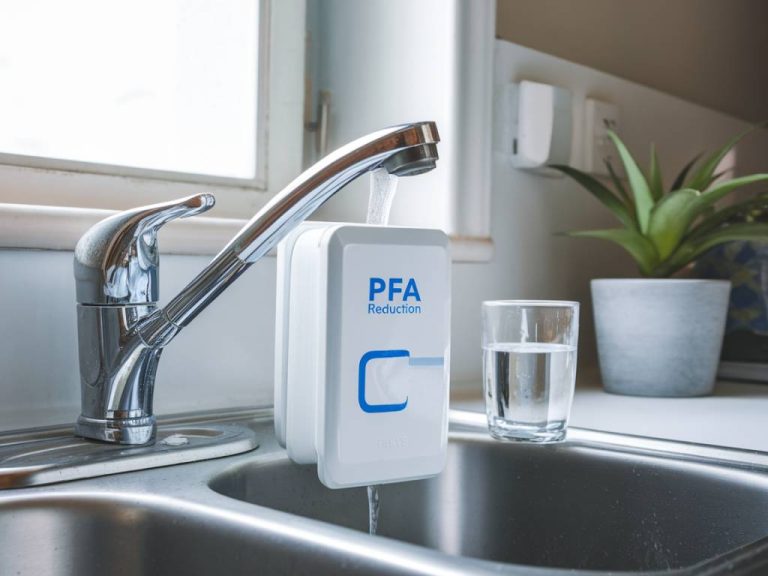
How pfas affect human health and what you need to know
Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances—better known as PFAS—are making headlines, and not for good reasons. Once dubbed « forever chemicals » due to their persistence in the environment, these synthetic compounds are now under scrutiny for their impact on human health. But what exactly are PFAS, and why should you be concerned? Understanding PFAS: What Are They? PFAS…

Understanding pfas in bottled water is it truly safe
Clean, fresh, and healthy. These are the words that often come to mind when you think about bottled water. But in recent years, concerns have been rising about the safety of bottled water due to the presence of PFAS, also known as ‘forever chemicals’. So, what exactly are PFAS, and should we be worried? Let’s…
Why water quality testing is essential for health
Water is essential to life, yet many of us often take its quality for granted. How often do you think about the water that pours from your taps each day? If you’ve never considered the importance of water quality testing, it’s time to start. This simple but crucial process is vital for ensuring the water…

Assessing the health impacts of long term pfas exposure
Understanding PFAS: What Are They? Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of man-made chemicals that have been used in a wide array of products for decades. From non-stick cookware to water-repellent clothing and firefighting foams, their presence is extensive. But as much as they’re known for their utility, PFAS are equally infamous for…

Pfas regulation updates and what they mean for consumers
Understanding PFAS and Their Impact As someone who deeply cares about health, fitness, and staying informed, you may have come across the term « PFAS » in recent news or discussions about environmental health. But what exactly are PFAS? Known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, these man-made chemicals have been used in various industrial and consumer products…

Water softener and its role in reducing pfas exposure
Water is essential to our daily lives, from quenching our thirst to preparing our meals. Yet, how often do we think about the quality of the water running through our taps? Recent discussions have revolved around PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) – those pesky chemicals that seem to stick around in our environment. But did…
- 1
- 2